How To Draw Sodium Chloride Crystal Structure
6.11A: Construction - Rock Table salt (NaCl)
- Page ID
- 2589
Rock salt also known as NaCl is an ionic compound. It occurs naturally equally white cubic crystals. The structure of NaCl is formed past repeating the unit prison cell. It has an organized structure and has a i:1 ratio of Na:Cl.
Introduction
Stone common salt (\(\ce{NaCl}\)) is an ionic chemical compound that occurs naturally as white crystals. Information technology is extracted from the mineral form halite or evaporation of seawater. The construction of NaCl is formed past repeating the face centered cubic unit cell. It has one:one stoichiometry ratio of Na:Cl with a molar mass of 58.4 thou/mol. Compounds with the sodium chloride construction include alikali halides and metal oxides and transition-metal compounds. An important role to many of import applications is structure and dynamics of h2o. Some applications include crystallization of proteins and conformational behavior of peptides and nucleic acids.
Construction
Figure \(\PageIndex{i}\) shows how the Na+ and Cl- ions occupy the infinite. The smaller ions are the Na+ with has an atomic radius of 102 pm, and the larger ions are the Cl- with an atomic radium of 181 pm. Since NaCl are ane to ane ratio as a compound, the coordination numbers of Na and Cl are equal. The larger green ions correspond Cl- and the smaller purple ions represent Na+. However, the structure of this molecule allows their positions to exist switched since the coordination numbers are equivalent.
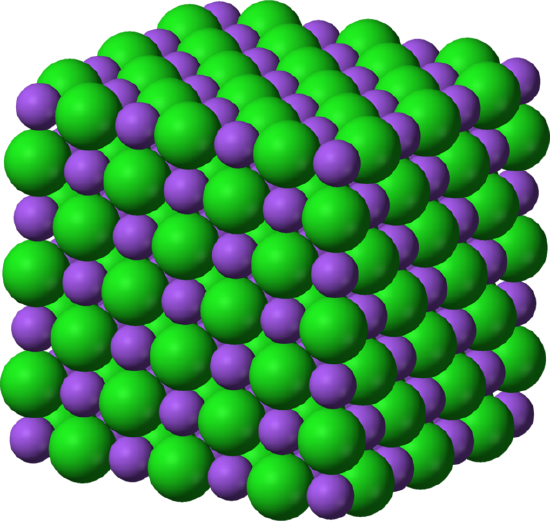
A Unit Cell
The unit of measurement jail cell of \(\ce{NaCl}\) consists of \(\ce{Na^{+}}\) ions and \(\ce{Cl^{-}}\) ions. There are iv types of site: unique primal position, face up site, edge sites and corner site, which are used to determine the number of Na+ ions and Cl- ions in the unit cell of NaCl. When counting the number of ions, a corner site would be shared by 7 other unit cells. Therefore, 1 corner would be 1/8 of an ion. A similar occurrence happens with the face site and the edge sites. For a face up site, information technology is shared past 1 other unit jail cell and for an edge site, the ion is shared by iii other unit cells. \(\ce{NaCl}\) is a face centered cubic unit prison cell which has 4 cations and four anions. This can exist shown by counting the number of ions and multiplying them in relation to their position.
- \(\ce{Na^{+}}\): \[1_{center} + 12_{border} \times \dfrac{one}{four} = 4\, \text{sodium ions full per cell} \nonumber\]
- \(\ce{Cl^{-}}\): \[4_{face} \times \dfrac{one}{2} + 8_{corner} \times \dfrac{ane}{eight} = 4\, \text{chloride ions full per cell} \nonumber\]
Each ion in this lattice has six of the other kind of ion equally its nearest neighbors, and twelve of the same kind of ions as its 2d nearest neighbors. There are many ionic compounds that assume this structure including all other halides of Na, Li, G and Rb. CsF, AgF, AgCl, BaO, CoO, and SrS are also amongst many that will course similar structures to NaCl.
References
- Gao, H.X., Fifty.-M. Peng, and J.M Zuo. "Lattice dynamics and Debye-Waller factors of some compounds with the sodium chloride structure." Acta Crystallographica: Section A (Wiley-Blackwell) 55.6 (1999): 1014. Academic Search Complete. EBSCO. Web.
- Housecroft, Catherine Due east., and Alan K. Sharpe. Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd ed. Harlow: Pearson Teaching, 2008. Print.
- Jun Soo, Kim, and Yethiraj Arun. "A Deviating Bibelot of H2o in Aqueous Sodium Chloride Solutions at Low Temperatures." Journal of Physical Chemical science B 112.6 (2008): 1729-1735. Academic Search Complete. EBSCO. Spider web.
Contributors and Attributions
- Michael Ford
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Map%3A_Inorganic_Chemistry_(Housecroft)/06%3A_Structures_and_energetics_of_metallic_and_ionic_solids/6.11%3A_Ionic_Lattices/6.11A%3A_Structure_-_Rock_Salt_(NaCl)
Posted by: harveyterfew1943.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Draw Sodium Chloride Crystal Structure"
Post a Comment